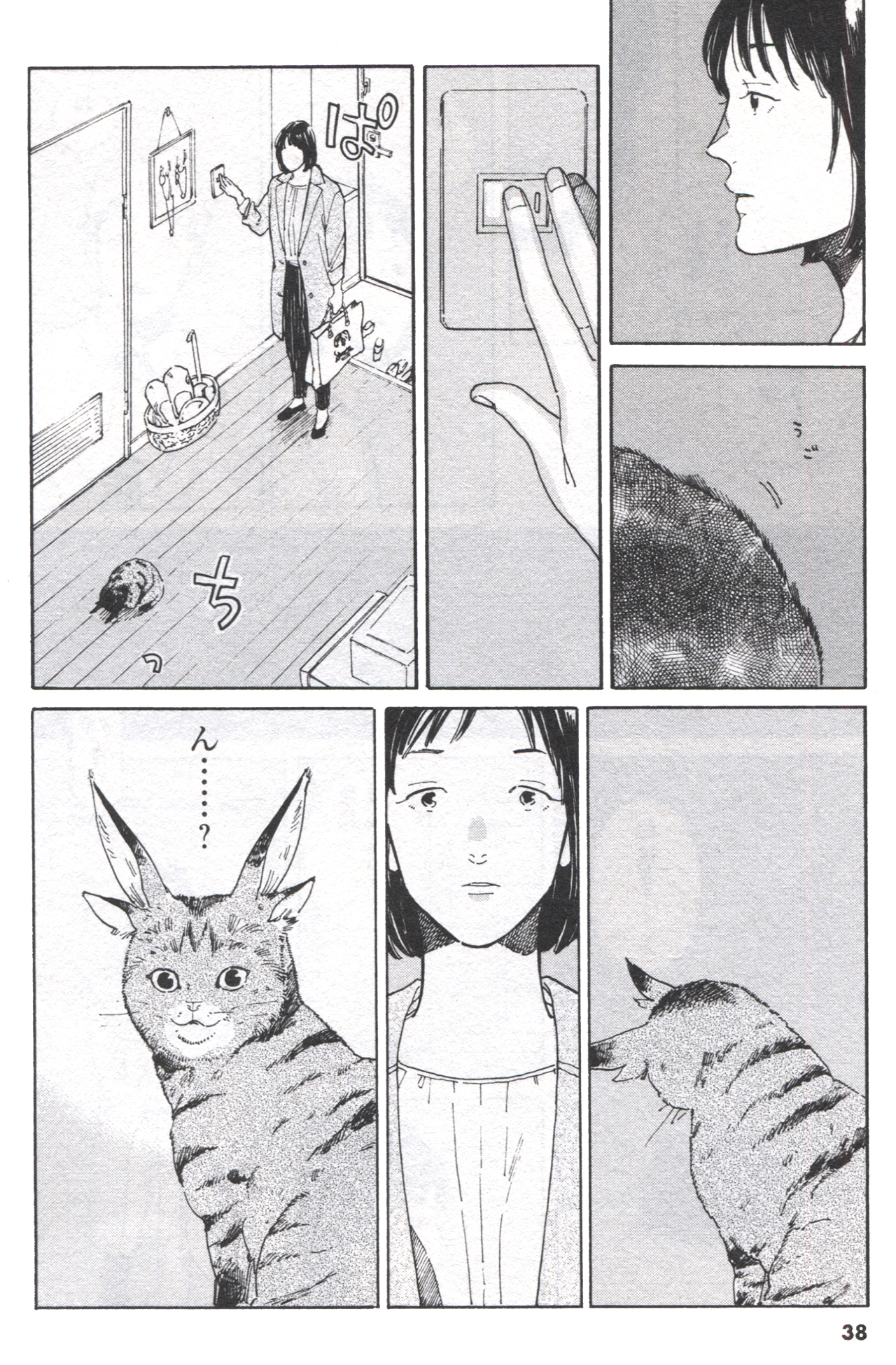
Kiyoshi Shigematsu’s The Blanket Cats collects seven stories about the clients of a service that rents cats for a period of three days. What I appreciate about these stories is that their human protagonists are messy people who are clearly the villain of someone else’s life. Will three days with a cat fix them? Probably not, to be honest, but it’s still a nice fantasy to imagine that a brief experience of caring for an animal could completely change someone’s perspective.
“The Cat in the Passenger Seat” is a frequent companion of Taeko, a woman on the verge of retirement who often rents this particular cat to accompany her on trips away from Tokyo. With no family to support her through a recent diagnosis of a serious illness, Taeko has decided to splurge on one final vacation. As for where the money has come from, it’s fair to say that Taeko is on the run from more than her worries about the future. She’s always done the right thing and made sacrifices for everyone else, so she might as well be selfish for once, right? Thankfully, Taeko’s cat companion helps her see beyond her immediate problems.
“The Cat with No Tail” is chosen by Koji, a boy in middle school whose growing pains have resulted in the first major crisis of his life. Instead of being bullied, he’s the one doing the bullying. Well, sort of. Koji tolerated an annoying classmate all throughout elementary school; and, now that he’s in a new environment, he finally found the courage to tell this kid to leave him alone. Unfortunately, he didn’t express himself in the most diplomatic way, and his former classmate was so distraught that he made a serious attempt at self-harm and almost died. That’s a wild thing to happen to a twelve-year-old, and Koji processes his guilt by talking to the cat, who responds by showing the emotions that Koji has been suppressing.
“The Cat Who Knew How to Pretend” is rented by Hiromi, a young woman who needs a stand-in for her family’s recently deceased pet in order to fool her grandmother, who’ll be visiting her parents’ house one final time before they entrust her to a facility that specializes in caring for patients living with cognitive decline. To ensure that the visit goes smoothly, Hiromi also asks her boyfriend to attend a family dinner even though she’s on the verge of breaking up with him. It’s all well and good for the cat to pretend that everything is fine, but Hiromi realizes that the time has come for her to be open and honest about what she wants.
I recently encountered the term “joyslop” as an appellation for low-effort entertainment media, and The Blanket Cats is joyslop if I’ve ever seen it. Psychological realism isn’t a concern in these stories, nor is animal welfare. Just so everyone is on the same page, “renting” an animal to any customer who walks through the door isn’t a great idea to begin with, and cats can’t be trained to accommodate different companions in the way that certain other domestic animals can. I apologize for being crude, but I imagine that the reality of a rental service like this would be cat piss everywhere. Still, The Blanket Cats is pure fantasy, like YA fiction for adults. It’s joyslop.
I’ve been thinking about the purpose served by The Blanket Cats and other cozy cat books, and I suspect their appeal probably extends a little deeper than simple guilty-pleasure reading. To varying degrees, the short stories collected in these books address fairly serious social issues such as, for example, dealing with school bullying as a parent or growing old without a social safety net. Books like The Blanket Cats provide a way to playact various scenarios from the comfort of your armchair – again, like YA fiction for adults.
I’m tempted to take this line of reasoning a few steps farther into social analysis and argue that the popularity of bestselling cat books might have something to do with the decline of “traditional” news media like print newspapers, morning radio broadcasts, and nightly news programs. I get the sense that, back when this sort of media was more widely consumed, journalists could provide authoritative editorial opinions of social issues, thus creating consensus and catharsis. In other words, a serious issue exists, but someone is talking about, and therefore someone must be doing something about it.
Now that our consumption of news is so fragmented, who knows what to think? People are still looking for an editorial voice to trust, and I feel like this is partially what’s behind the success of books like The Blanket Cats. The fantasy of these non-confrontational stories about normal people dealing with hot-topic social issues isn’t necessarily that a cat is going to fix you in three days, but rather that these systemic issues can be fixed, because someone is talking about them. All things considered, The Blanket Cats is much easier to consume than, say, a political podcast hosted by wealthy kids in Brooklyn or a series of inflammatory diatribes posted to YouTube.
In any case, I’d like to express my appreciation for the translator, Jesse Kirkwood, who has found himself a lovely (and hopefully fruitful) niche in translating and localizing this sort of fiction, often through the charming vernacular of light Briticisms. This style of casual prose in Japanese requires no small amount of skill to render into the sort of English suited for a mass-market bestseller. I’ve been following Kirkwood’s work since his translation of A Perfect Day to Be Alone, and I’m always impressed.
If you’re in the market for cozy cat fiction, The Blanket Cats has more of a bite than the usual fare, but it’s still sweet and hopeful. This book hopes you’re doing okay. If you’re reading this review, I hope you’re doing okay too. After all, there’s definitely a place for joyslop in the world, and there’s no shame in needing a cat and blanket sometimes.